Java Source Code
java.lang
Object 1
1 | public final void wait(long timeout, int nanos) throws InterruptedException { |
String 1
- jdk1.8及以前String使用的是char数组,jdk1.9及以后使用的是byte数组。
- 拥有equals()和hashcode()方法
hashCode()
1 | public int hashCode() { |
Equals()
1 | public boolean equals(Object anObject) { |
AbstractStringBuilder 1
System.arraycopy
1 | public AbstractStringBuilder delete(int start, int end) { |
str.getChars
1 | public AbstractStringBuilder replace(int start, int end, String str) { |
Surrogate Pairs
1 | private void reverseAllValidSurrogatePairs() { |
- Unicode
StringBuffer 1
- Multiple Threads
transient
1 | private transient char[] toStringCache; |
- 一旦变量被transient修饰,变量将不再是对象持久化的一部分,该变量内容在序列化后无法获得访问。
- transient关键字只能修饰变量,而不能修饰方法和类。注意,本地变量是不能被transient关键字修饰的。变量如果是用户自定义类变量,则该类需要实现Serializable接口。
- 被transient关键字修饰的变量不再能被序列化,一个静态变量不管是否被transient修饰,均不能被序列化。
StringBuilder 1
- Single Thread
- 线程不安全,但效率高
StringLatin 1
1 | public static int indexOf(byte[] value, int valueCount, byte[] str, int strCount, int fromIndex) { |
Boolean 2
getBoolean(String name)
1 | public static boolean getBoolean(String name) { |
当且仅当以参数命名的系统属性存在,且等于 “true” 字符串时,才返回 true。
Byte 2
Double 2
Float 2
Integer 2
Long 2
Short 2
Thread 2
native
1 | private static native void registerNatives(); |
- 编写带有native声明的方法的Java类(java文件)
- 使用javac命令编译编写的Java类(class文件)
- 使用javah -jni 来生成后缀名为.h的头文件(.h的文件)
- 使用其他语言(C、C++)实现本地方法
- 将本地方法编写的文件生成动态链接库(dll文件)
clone()
1 | protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { |
join()
Waits at most millis milliseconds for this thread to die.
主线程等待wait()当前子线程运行结束。
ThreadLocal 2
Enum 3
Throwable 3
Error 3
Exception 3
Class 4
ClassLoader 4
Compiler 4
System 4
Package 4
Void 4
java.util
AbstractList 1
get()
1 | abstract public E get(int index); |
- 唯一的抽象方法
AbstractMap 1
put()
1 | public V put(K key, V value) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException();} |
AbstractSet 1
ArrayList 1
EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
1 | private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { if (initialCapacity > 0) { this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; } else if (initialCapacity == 0) { this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity); }}public ArrayList() { this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;} |
- EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA,优化创建ArrayList空实例时产生不必要的空数组,使得所有ArrayList空实例都指向同一个空数组。
- DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA,确保无参构成函数创建的实例在添加第一个元素时,最小的容量是默认大小10。
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE
1 | private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; |
grow(int minCapacity)
1 | int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);jdk1.6:int newCapacity = (oldCapacity * 3)/2 + 1; |
- 最小容量扩容至原有的1.5倍
- 考虑了可能的整型溢出问题
minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win
toArray()
1 | public Object[] toArray() { return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); |
This method acts as bridge between array-based and collection-based APIs.
elementData[–size] = null;
clear to let GC do its work
- 为了让GC起作用,必须显式的为最后一个位置赋值null。
SubList
Returns a view of the portion of this list between the specified fromIndex, inclusive, and toIndex, exclusive.
1 | public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) { subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size); return new SubList(this, 0, fromIndex, toIndex);} |
- subList方法返回的是一个视图SubList,即对源列表的映射,如果对其进行编辑操作,源列表也会受到影响。
1 | private class SubList extends AbstractList<E> implements RandomAccess { private final AbstractList<E> parent; private final int parentOffset; private final int offset; int size; ...} |
- SubList是一个ArrayList的内部类。
- SubList中没有数组、列表等属性来存储数据。
1 | private void checkForComodification() { if (ArrayList.this.modCount != this.modCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException();} |
- SubList进行添加、删除元素会抛出异常ConcurrentModificationException,触发fail-fast机制。
LinkedList 1
node(int index)
1 | Node<E> node(int index) { // assert isElementIndex(index); if (index < (size >> 1)) { Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; } else { Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; }}public E get(int index) { checkElementIndex(index); return node(index).item;} |
- 判断index位于链表前半部分还是后半部分
removeFirst()
1 | public E remove() { return removeFirst();}public E pop() { return removeFirst();}public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) { return remove(o);}public E removeFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; if (f == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return unlinkFirst(f);}private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) { ...} |
- 公私分明
addLast(E e)
1 | public void addLast(E e) { linkLast(e);}public boolean add(E e) { linkLast(e); return true;} |
isElementIndex(int index)
1 | /** * Tells if the argument is the index of an existing element. */private boolean isElementIndex(int index) { return index >= 0 && index < size;}/** * Tells if the argument is the index of a valid position for an * iterator or an add operation. */private boolean isPositionIndex(int index) { return index >= 0 && index <= size;} |
HashMap 1
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY
1 | static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16 |
- 默认容量,也即数组长度。
- 容量必须是2的次数幂,因为在查找hash地址时,会进行取模位运算。
TREEIFY_THRESHOLD
1 | static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8; |
- 当链表长度超过阈值时,会将链表转换为红黑树,使HashMap的性能得到进一步提升。
hash(Object key)
1 | static final int hash(Object key) { |
- key值进行hashcode以后,进行相与时候都是只用到了后四位,前面的很多位都没有能够得到使用,这样也可能会导致生成的下标值不能够完全散列。
- 将生成的hashcode值的高16位于低16位进行异或运算,这样得到的值再进行相与,得到最散列的下标值。
tableSizeFor(int cap)
1 | static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) { int n = cap - 1; n |= n >>> 1; n |= n >>> 2; n |= n >>> 4; n |= n >>> 8; n |= n >>> 16; return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;} |
- 反复操作把每一位数变成1。
- 最后+1变成最近的2多整数次幂。
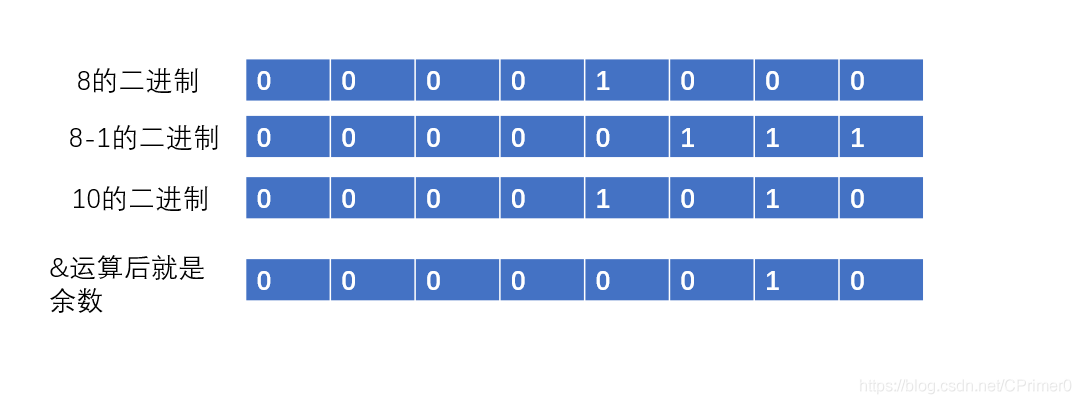
i = (n - 1) & hash
$$
(n - 1) & hash = hash % n
$$
- n为2多整数次幂,n-1即为全1位数。
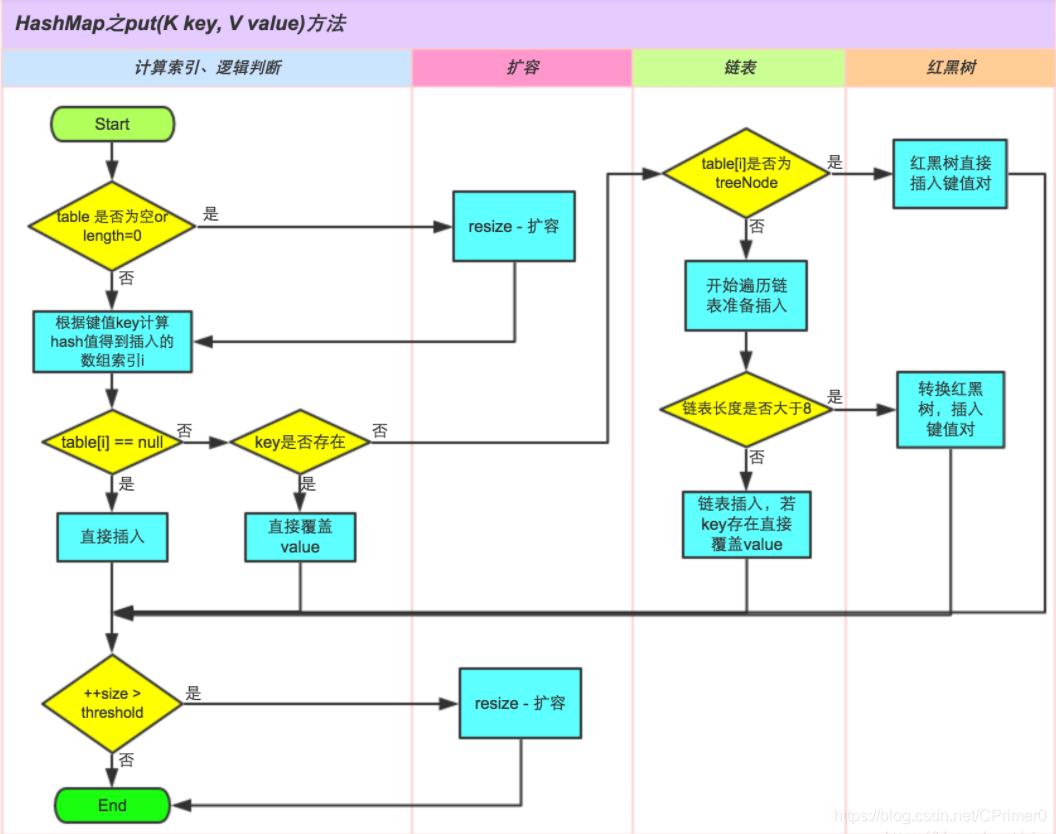
putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict)
Hashtable 1
it is recommended to use HashMap in place of Hashtable. If a thread-safe highly-concurrent implementation is desired, then it is recommended to use java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap in place of Hashtable.
threshold
1 | public Hashtable() { this(11, 0.75f);}int newCapacity = (oldCapacity << 1) + 1; |
- 默认的初始大小为11,之后每次扩充为原来的2n+1。
- 会尽量使用素数、奇数作为容量的大小,使得简单取模的哈希结果会更加均匀。
abstract class Dictionary<K,V>
- 已过时
This class is obsolete. New implementations should implement the Map interface, rather than extending this class.
interface Enumeration<E>
1 | public synchronized Enumeration<K> keys() { return this.<K>getEnumeration(KEYS);}public synchronized Enumeration<V> elements() {return this.<V>getEnumeration(VALUES);} |
- 已被迭代器重写,甚少被使用。
The functionality of this interface is duplicated by the Iterator interface.
1 | default Iterator<E> asIterator() { return new Iterator<>() { public boolean hasNext() { return hasMoreElements(); } public E next() { return nextElement(); } };} |
- 可以使用方法asIterator()转换为迭代器。
It is possible to adapt an Enumeration to an Iterator by using the asIterator method.
(hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length
- 相比hashmap,采用了直接取模。
- hash值和0x7FFFFFFF进行一次按位与操作,是为了保证得到的index的第一位为0,也就是为了得到一个有符号正数。
HashSet 1
PRESENT
1 | private static final Object PRESENT = new Object(); public boolean add(E e) { return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;} |
- 定义一个static finall的Object对象作为HashMap的虚拟的value。
LinkedHashMap
1 | HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean dummy) { map = new LinkedHashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);}public HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { map = new HashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);} |
- 只被用来创建LinkedHashSet的私有方法。
- dummy参数用来区分其他(int float)构造函数
LinkedHashMap 1
accessOrder
1 | final boolean accessOrder;public LinkedHashMap() { super(); accessOrder = false;} |
- accessOrder=false,按照插入元素的顺序遍历元素。
- accessOrder=true,按照访问元素的顺序,即可实现最近最少使用策略(Least Recently Used,LRU)。
removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K,V> eldest)
1 | protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K,V> eldest) { return false;} |
- 移除最早加入的Entry。
- 默认不使用,但允许覆写。
afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e)
- 在节点访问之后被调用,主要在put()已经存在的元素或get()时。
- 如果accessOrder=true,把当前访问节点移动到双向链表的末尾。
LinkedHashSet 1
LinkedHashMap
1 | public LinkedHashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { super(initialCapacity, loadFactor, true);}HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean dummy) { map = new LinkedHashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);} |
- 底层调用LinkedHashMap实现。
TreeMap 1
继承NavigableMap,提供访问给定搜索目标的最接近匹配项的导航方法。
继承SortedMap,保证key有序性。
TreeSet 1
- 底层为TreeMap
Vector 2
- 线程安全,开销增大
Queue 2
- 继承自Collection
- 提供两类方法
| Throws exception | Returns special value | |
|---|---|---|
| Insert | add(e) | offer(e) |
| Remove | remove() | poll() |
| Examine | element() | peek() |
Stack 2
- 继承自Vector
- 建议使用Deque
SortedMap 2
- 提供有序性的方法
SortedSet 2
Spliterators
- 并行迭代器
Collections 3
binarySearch
1 | private static <T>int indexedBinarySearch(List<? extends Comparable<? super T>> list, T key) { int low = 0; int high = list.size()-1; while (low <= high) { int mid = (low + high) >>> 1; Comparable<? super T> midVal = list.get(mid); int cmp = midVal.compareTo(key); if (cmp < 0) low = mid + 1; else if (cmp > 0) high = mid - 1; else return mid; // key found } return -(low + 1); // key not found} |
- Arrays 3
- Comparator 3
- Iterator 3
- Base64 4
- Date 4
- EventListener 4
- Random 4
- SubList 4
- Timer 4
- UUID 4
- WeakHashMap 4
3、java.util.concurrent
ConcurrentHashMap 1
Executor 2
AbstractExecutorService 2
ExecutorService 2
ThreadPoolExecutor 2
BlockingQueue 2
7)AbstractQueuedSynchronizer 2
8)CountDownLatch 2
- FutureTask 2
10)Semaphore 2
11)CyclicBarrier 2
13)CopyOnWriteArrayList 3
14)SynchronousQueue 3
15)BlockingDeque 3
- Callable 4
4、java.util.concurrent.atomic
AtomicBoolean 2
AtomicInteger 2
AtomicLong 2
AtomicReference 3
5、java.lang.reflect
Field 2
Method 2
6、java.lang.annotation
Annotation 3
Target 3
Inherited 3
Retention 3
Documented 4
ElementType 4
Native 4
Repeatable 4
7、java.util.concurrent.locks
Lock 2
Condition 2
ReentrantLock 2
ReentrantReadWriteLock 2
8、java.io
File 3
InputStream 3
OutputStream 3
Reader 4
Writer 4
9、java.nio
Buffer 3
ByteBuffer 4
CharBuffer 4
DoubleBuffer 4
FloatBuffer 4
IntBuffer 4
LongBuffer 4
ShortBuffer 4
10、java.sql
Connection 3
Driver 3
DriverManager 3
JDBCType 3
ResultSet 4
Statement 4
11、java.net
Socket 3
ServerSocket 3
URI 4
URL 4
URLEncoder 4